Ecommerce Unboxed - The Basics of the Business
Electronic commerce, or Ecommerce, is a term used to describe entities that buy and sell goods and services online. In today’s market, nearly any and every product or service can be sold online.
The history of Ecommerce dates back to 1994 and since then has evolved into an industry that did more than $870 billion in the United States in 2021. Today, Ecommerce includes massive corporations, small businesses, and independent freelancers, all using the internet to their advantage to reach new customers from all over the globe.
So, what is Ecommerce and what can you do with your insights to grow your business?
| Understanding Ecommerce |
What Is Ecommerce?
Ecommerce is a term used to encompass any type of online sale of goods or services. However, Ecommerce is about more than just buying a sweater over the internet and it has grown into one of the largest, and fastest growing, industries on the planet today.
In fact, according to one study from SalesForce, approximately 56% of organizations expect a majority of their revenue to come from Ecommerce within the next three years. And these numbers are only growing.
While Ecommerce started on a desktop computer and involved the online sale of a Sting CD, today, more than half of all Ecommerce sales are done through mobile phones. Whether you are looking to learn more about Ecommerce as a seller, buyer or advertising, it’s important to understand how this industry works and how its changing in our market today.
What Are the Different Types of Ecommerce Models?
There are five common types of Ecommerce models that can be used to describe the vast majority of online transactions.
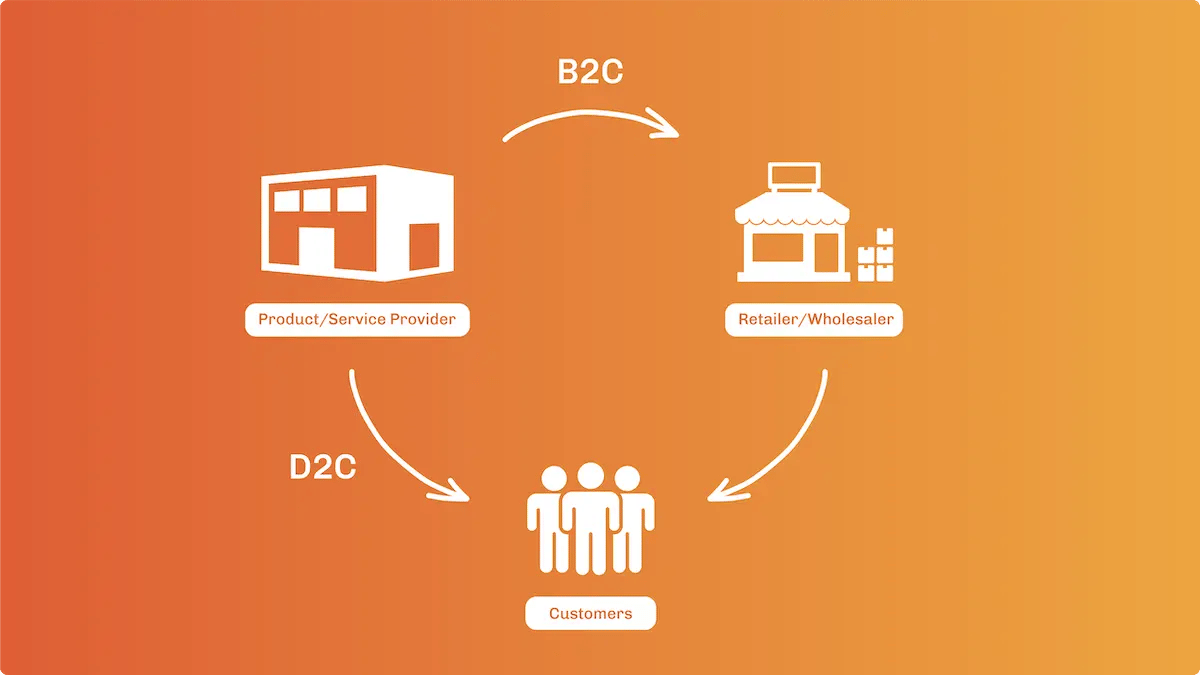
Business to Consumer (B2C)
One of the most common Ecommerce models, B2C involves the sale of goods to consumers through retail outlets and wholesalers.
Direct to Consumer (D2C)
This type of Ecommerce site involves a manufacturer selling goods or services directly to an individual consumer. For example, if you buy shoes from the original manufacturer's website.
Note: B2C and DTC are often used interchangeably, however, they are different models.
Business to Business (B2B)
A B2B Ecommerce company occurs when a business sells a good or service to another business. For example, a business that sells invoicing software to other businesses.
Consumer to Consumer (C2C)
A C2C Ecommerce company describes a situation where a consumer sells a good or service to another consumer. For example, when you sell something to another person on Facebook Marketplace.
Consumer to Business (C2B)
This type of Ecommerce situation involves a consumer selling their own products or services to an organization. For example, influencers who offer to promote a product on their social media account for a fee.
What Are Examples of Ecommerce Transactions?
The aforementioned Ecommerce businesses typically perform one of these four types of transactions.
- Retail transactions. These transactions involve the sale of a product by a business directly to the customer.
- Physical product transactions. This term is used to describe any tangible good that is physically shipped to customers and needs to be replenished after sales are made.
- Digital product transactions. Any product that is sold for consumption or licensed for use. It isn’t a physical product but can be downloaded digitally over the internet.
- Service-based transactions. A skill or set of skills that are provided online in exchange for compensation. You purchase a service provider’s time for a fee.
What Are Examples of Ecommerce Revenue Models?
As the Ecommerce industry continues to grow, there is no shortage of different types of Ecommerce companies out there. Here are some of the most common examples of Ecommerce revenue models.
Drop Shipping
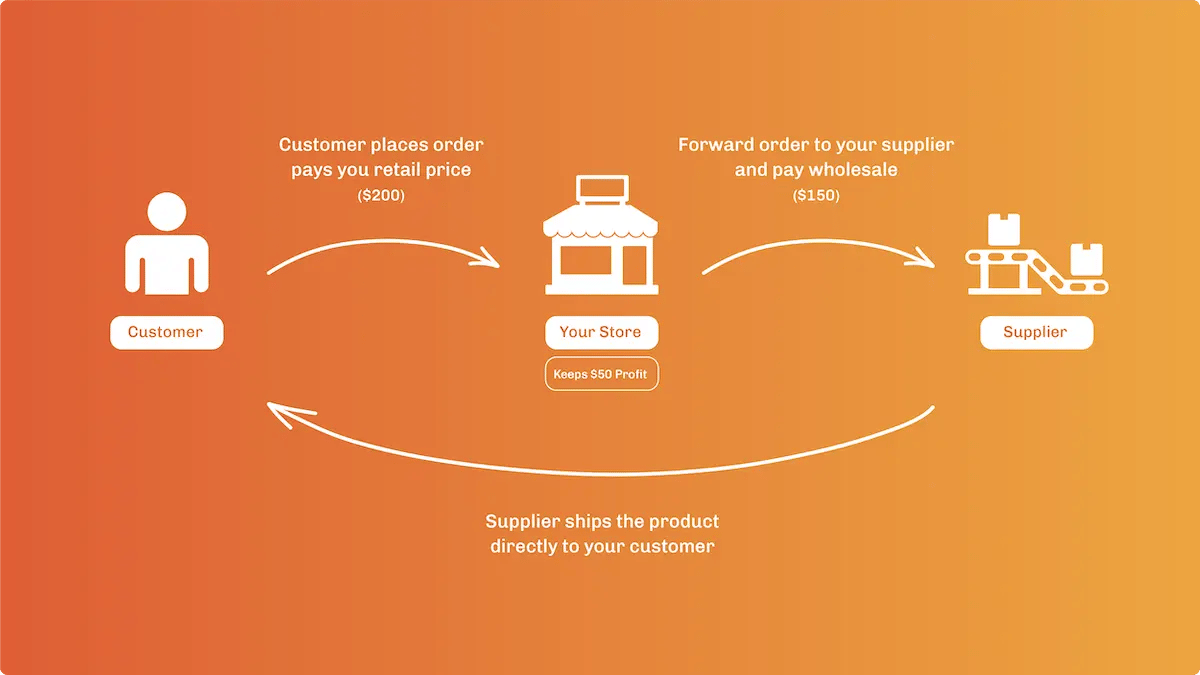
The term Drop Shipping describes the sale of a product, which is manufactured and shipped directly to the consumer by a third party. It is often seen as one of the easiest forms of Ecommerce, as it allows companies to create digital storefronts, generate sales, and collect digital currency without having to stock any items themselves.
Once the sale is made, the Ecommerce store passes on the order to a “drop ship supplier” who manages inventory, oversees warehouses, and delivers the product directly to the consumer.
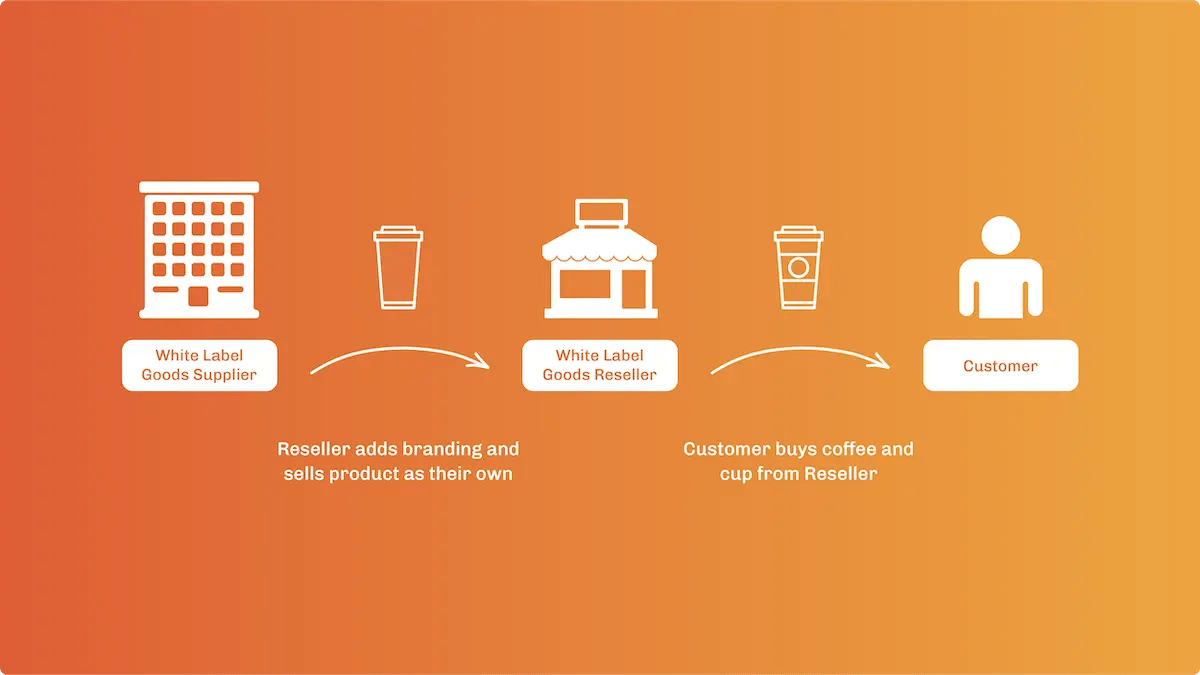
White Labeling
White label Ecommerce companies leverage products that are already successful and sold by another company to build their business. After a customer places an order, the Ecommerce company receives the existing product, repackages it with their own label, and distributes the product to the customer directly.
While there is little control on the company’s part, they have hardly any in-house manufacturing costs and restraints.
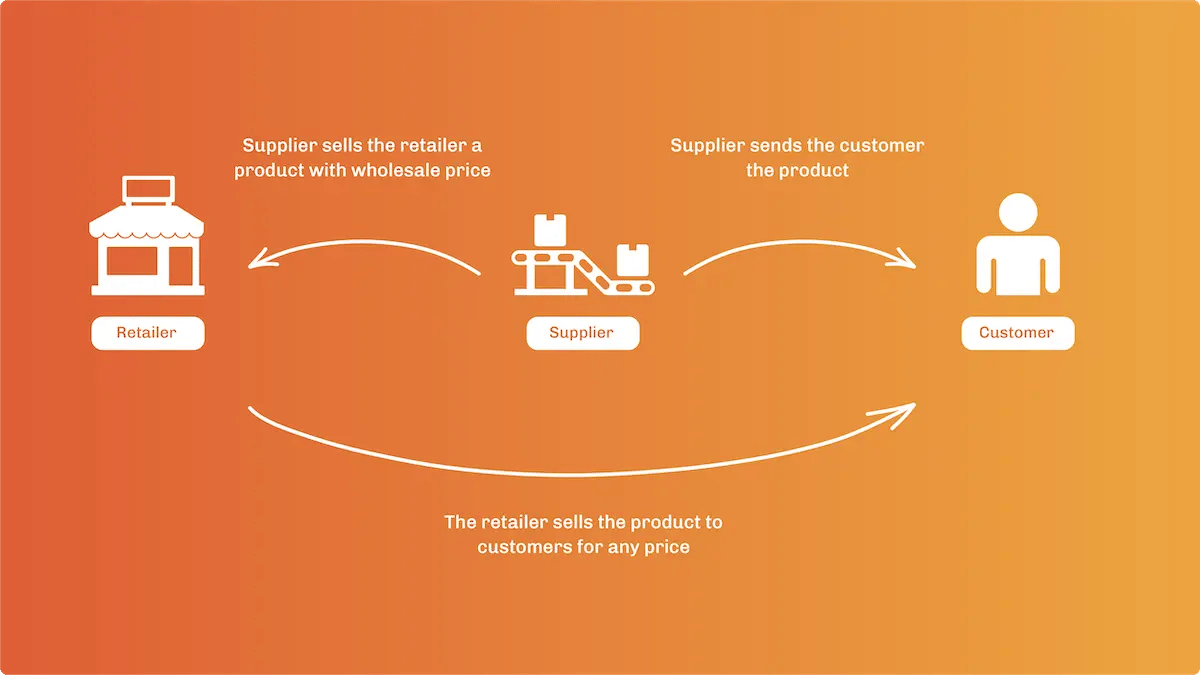
Wholesaling
Wholesaling involves the sale of products in bulk to a retailer that will sell these products to consumers. Wholesalers often have bulk pricing for retailers for a lower cost than they would charge consumers for single-unit prices. Running a wholesale business involves maintaining large quantities of products in a warehouse.
Private Labeling
Private labeling is a growing Ecommerce approach for businesses that don’t have large upfront capital or their own factory space to manufacture their own goods. These companies send a plan to a contracted manufacturer who makes the product. This manufacturer may also be able to ship the product directly to the customer.
Typically, companies that take this approach receive on-demand owners with little turnaround times and can’t cover all of the expenditures to fulfill these expenses on their own.
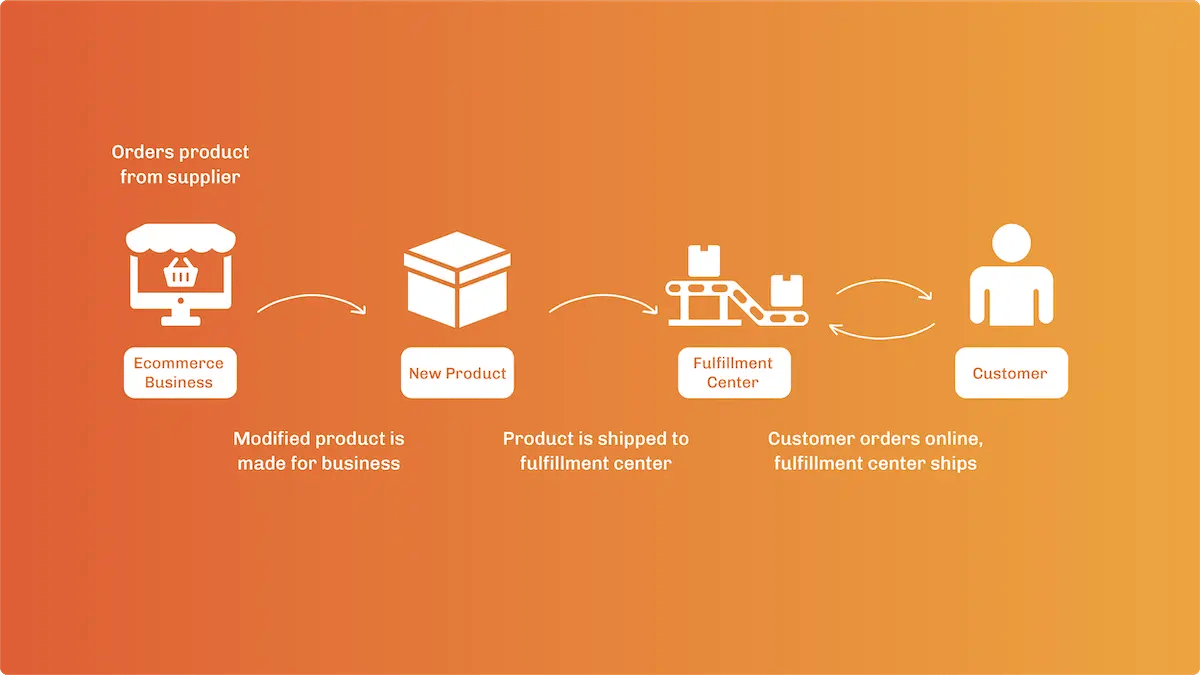
Subscription Services
Subscription services involve the automatic recurring purchase of a product or service regularly until the subscriber decides to cancel. This type of service leverages loyal customers and takes the time and effort out of placing repeat orders. Typically, orders ad incentivized with lower prices as well.
While some companies create boxes of products for their customers to try, others will set up repeat orders for products like soap or razors, so shoppers can automatically get the items they need, before they remember to order them.
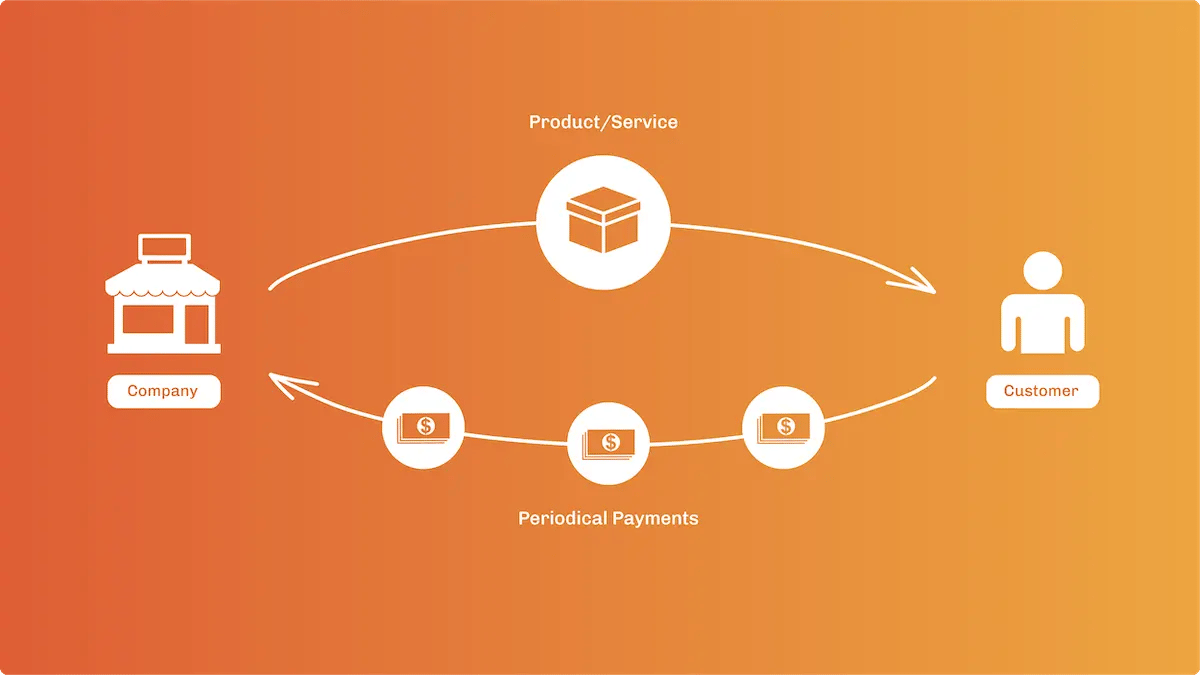
Crowdfunding
The crowdfunding process involves collecting money from consumers in advance of a product being available for purchase. The goal of crowdfunding is to raise the necessary startup capital to bring a product to the market. Typically, interested customers will place an order and “pay” for their product ahead of time, and get some type of incentive or benefit as being part of the crowdfunding process.
If the company reaches its goal of getting enough capital, the consumer gets their product delivered in the mail as soon as they can create the concept.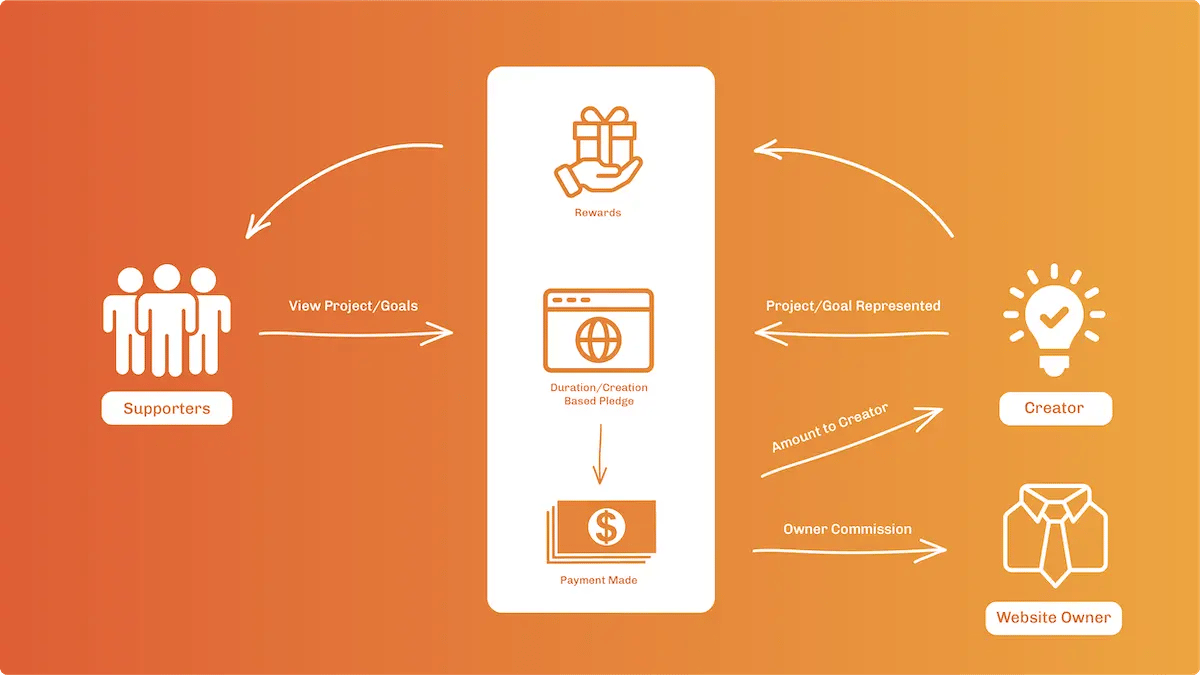
Conclusion
These types of businesses all represent the most common ways Ecommerce companies make money today.
The bottom line is that Ecommerce is just one component of running a successful online business and describes the process of selling any type of good or service over the internet. In the past 30 years, Ecommerce has gone from a relatively unknown type of transaction to one of the biggest industries in the world, encompassing dozens of different types of transactions.
Together, businesses like these operating in the Ecommerce world have forever changed the way consumers today shop for and purchase the products and services they need the most.
 You've made it this far and you've learned so much. Congratulations!
You've made it this far and you've learned so much. Congratulations!
If you're looking to learn more about marketing or Ecommerce in general, feel free to reach out to us at: solutions@undigital.com
You May Also Like
These Related Stories
A Brief History of Ecommerce

Ecommerce Inventory Management Strategies


